Testing UDP can be tricky and confusing: few apps support it, SOCKS5 requires a separate UDP ASSOCIATE handshake to relay datagrams, and browsers neither expose raw UDP sockets nor forward UDP‐based transports like QUIC (HTTP/3) through proxies.
For this reason, we’ve put together a few different ways to test whether your SOCKS5 server is proxying UDP.

When UDP Is Used in Practice
These are some of the real-world environments in which UDP is used:
- DNS Queries: These work over UDP and uses port 53, can be tested using
dig @8.8.8.8 google.com - Network Time Protocol: NTP uses UDP and works on port 123, can be tested using
ntpd -q time.google.com - Voice-over-IP Apps: Slack, Teams, Skype, Zoom, Discord, and more all use UDP to facilitate VoIP
- Online games and live streaming apps
This isn’t an exhaustive list, but these are some key examples we’ll leverage to run our tests, alongside a custom script.
IP rotation, city and carrier targeting,
sticky sessions — control it all via API

Setting up the Tunnel
In order to test whether our SOCKS proxy successfully proxies our UDP traffic, we first need to install tun2socks to create a virtual interface that will forward all our traffic (UDP and TCP) over a SOCKS5 proxy.
You can download the binary from Github.
Setting up the Tunnel on Linux
First, let’s create TUN interface tun0 and assign an IP address for it:
ip tuntap add mode tun dev tun0
ip addr add 198.18.0.1/15 dev tun0
ip link set dev tun0 upNext, configure the default route table with different metrics. Let’s say the primary interface is eth0 and gateway is 192.168.0.1.
Important Note: Make sure you’re connected to the server via LAN and make sure the values are correct, otherwise you will lose access to the server.
ip route del default
ip route add default via 198.18.0.1 dev tun0 metric 1
ip r add default via 192.168.0.1 dev eth0 metric 10Now all traffic will go through the new TUN interface then to the proxy.
Once you’re done testing:
- Remove the new
tun0routes - Add the default
eth0route again (tun2socks might have deleted it)
Setting up the Tunnel on MacOS
For macOS, we need to start tun2socks first so that it will create a TUN interface for us.
tun2socks -device utun123 -proxy socks5://username:password@IP:PORT -interface en0Your Internet interface name might be different than en0. Use ifconfig to find the correct name.
Next, let’s use ifconfig to bring the TUN interface up and assign addresses for it.
sudo ifconfig utun123 198.18.0.1 198.18.0.1 upAdd these specific routes so that tun2socks can handle primary connections.
sudo route add -net 1.0.0.0/8 198.18.0.1
sudo route add -net 2.0.0.0/7 198.18.0.1
sudo route add -net 4.0.0.0/6 198.18.0.1
sudo route add -net 8.0.0.0/5 198.18.0.1
sudo route add -net 16.0.0.0/4 198.18.0.1
sudo route add -net 32.0.0.0/3 198.18.0.1
sudo route add -net 64.0.0.0/2 198.18.0.1
sudo route add -net 128.0.0.0/1 198.18.0.1
sudo route add -net 198.18.0.0/15 198.18.0.1Now all traffic will go through the new TUN interface then to the proxy.
Once you’re done testing, just exit the command and it will automatically delete the new routes.

Testing UDP Traffic over SOCKS5
Test UDP with DNS Query
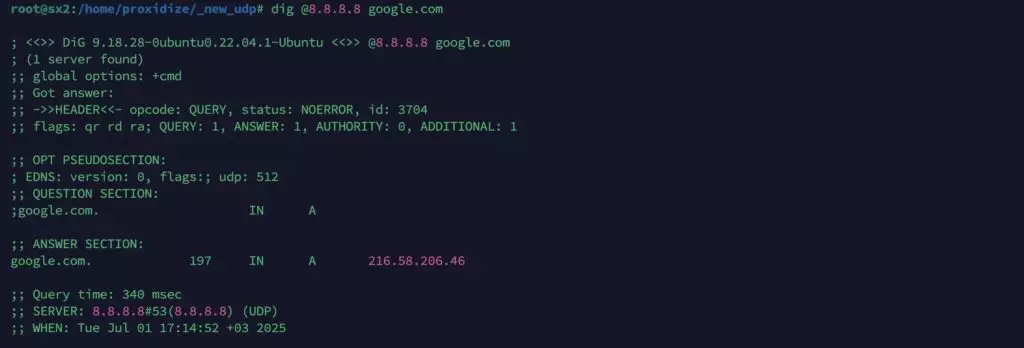
Use the DNS lookup utility to send a query to the DNS server at 8.8.8.8 (which is Google’s public resolver) instead of your system’s default one to ping Google’s homepage.
Command: dig @8.8.8.8 google.com. It’s the same command on Linux and MacOS
Success: Returned the IP behind google.com using a proxy that supports UDP.
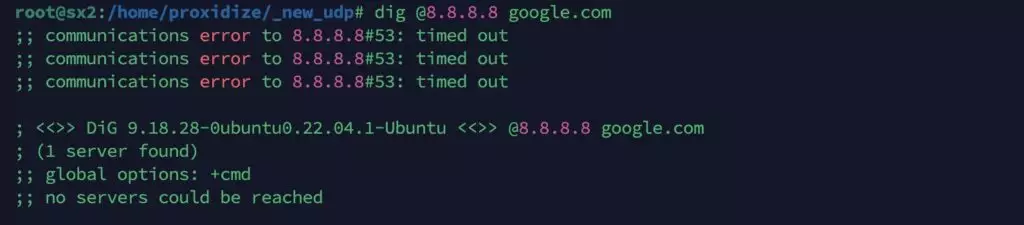
Failure: Timeout because the proxy does not support UDP.
Test UDP with NTP
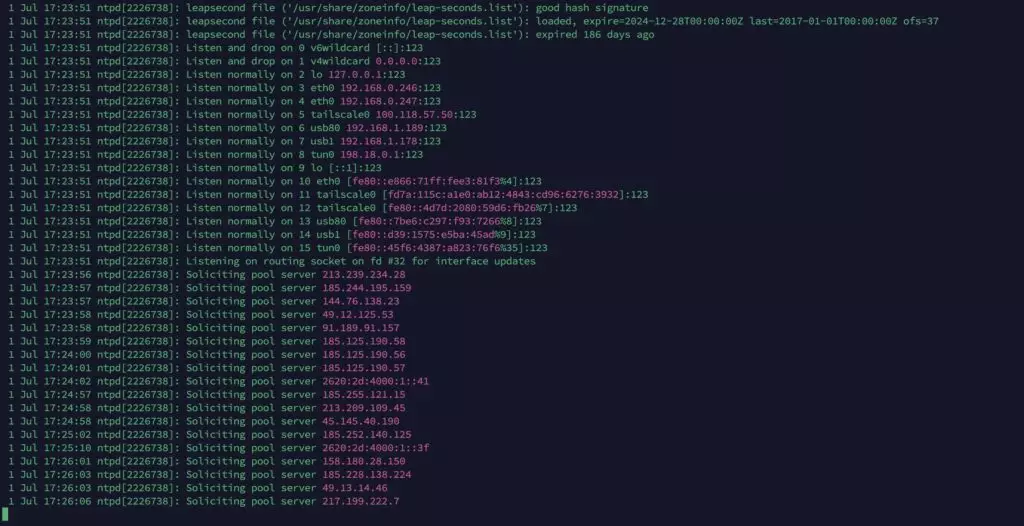
Given that NTP traffic is entirely over UDP, sending ntpd -q time.google.com through your SOCKS5 proxy is another way to test whether it supports UDP.
Command: sudo ntpd -q time.google.com (Linux only). This might require installing ntp.
Success: It was able to send/receive and resolve Google’s time server.
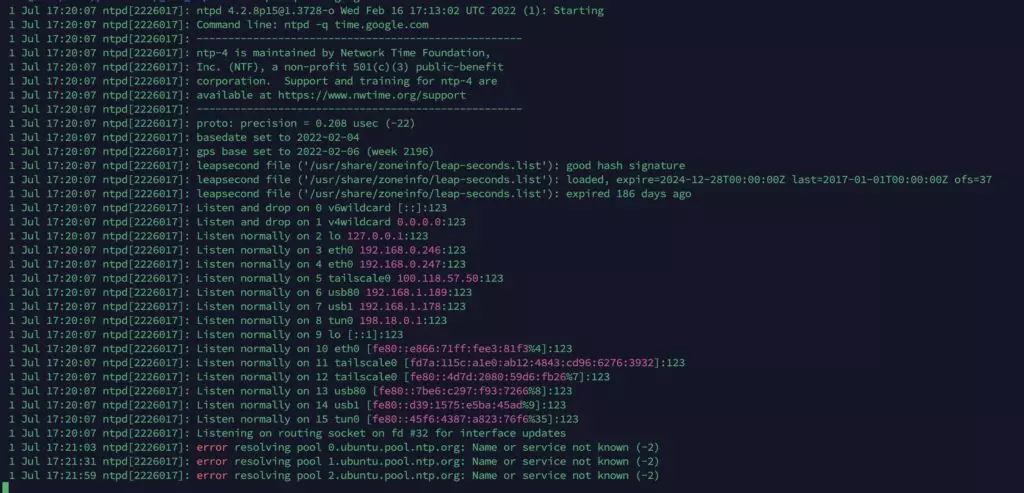
Failure: It was not able to resolve over the proxy.
Test UDP with Discord VoIP
VoIP uses UDP to carry its real-time audio and video. By joining a Discord call or voice channel and successfully being able to hear others and have others hear you, it confirms that UDP is being carried over your SOCKS proxy.
- Download the Discord desktop client
- Connect to any voice channel
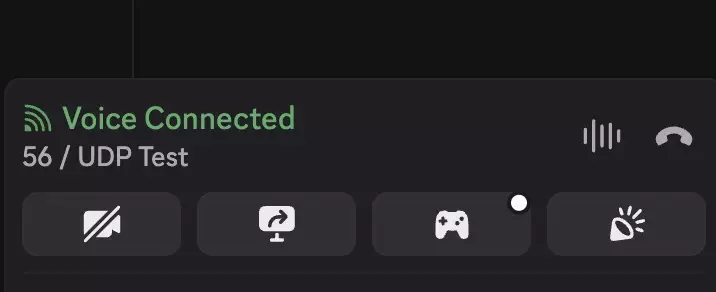
Success: Displays “Voice connected” and others in the channel are able to hear you.
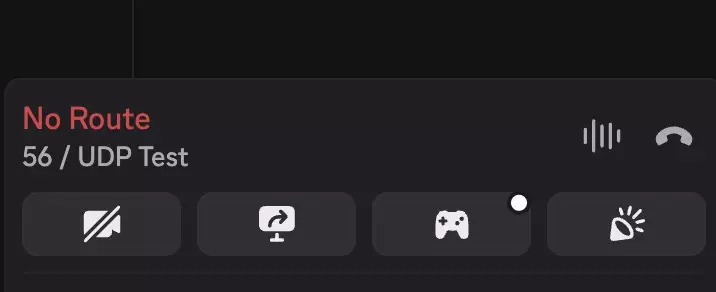
Failure: You can’t hear anyone in the voice channel and your connection shows “No Route”.
Test UDP over SOCKS with Custom UDP Client Script
Testing UDP over SOCKS for dozens — if not hundreds — of proxies can be very time consuming. Instead of doing it all manually, we’ve created a custom script that tests UDP traffic via Google DNS query for you. We’ve included a link so you can download and test your own IPs for yourself.
For the script to work you need to:
- Have python3 installed
- Create a proxy.txt file that lists your proxies in the following format: username:password@host:port or host:port if it has no authentication
- Run the script via python3 test_udp.py
import base64
import socket
import struct
import sys
import time
from typing import Optional, Tuple
class SOCKS5UDPTester:
def __init__(
self,
proxy_host: str,
proxy_port: int,
username: str = None,
password: str = None,
):
self.proxy_host = proxy_host
self.proxy_port = proxy_port
self.username = username
self.password = password
self.sock = None
def connect_and_authenticate(self) -> bool:
"""Establish connection and authenticate with SOCKS5 proxy"""
try:
self.sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.sock.settimeout(10)
self.sock.connect((self.proxy_host, self.proxy_port))
# SOCKS5 greeting
if self.username and self.password:
# Request username/password authentication
greeting = b"\x05\x02\x00\x02" # SOCKS5, 2 methods, no auth + username/password
else:
# Request no authentication
greeting = b"\x05\x01\x00" # SOCKS5, 1 method, no auth
self.sock.send(greeting)
response = self.sock.recv(2)
if len(response) != 2 or response[0] != 0x05:
print("❌ Invalid SOCKS5 greeting response")
return False
auth_method = response[1]
if auth_method == 0x00: # No authentication
print("✅ Connected with no authentication")
return True
elif auth_method == 0x02: # Username/password
return self._authenticate_userpass()
else:
print(f"❌ Unsupported authentication method: {auth_method}")
return False
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Connection failed: {e}")
return False
def _authenticate_userpass(self) -> bool:
"""Perform username/password authentication"""
if not self.username or not self.password:
print("❌ Username/password required but not provided")
return False
# Username/password authentication request
username_bytes = self.username.encode("utf-8")
password_bytes = self.password.encode("utf-8")
auth_request = struct.pack("!BB", 0x01, len(username_bytes))
auth_request += username_bytes
auth_request += struct.pack("!B", len(password_bytes))
auth_request += password_bytes
self.sock.send(auth_request)
auth_response = self.sock.recv(2)
if len(auth_response) != 2 or auth_response[0] != 0x01:
print("❌ Invalid authentication response")
return False
if auth_response[1] == 0x00:
print("✅ Authentication successful")
return True
else:
print("❌ Authentication failed")
return False
def test_udp_associate(self) -> Tuple[bool, Optional[Tuple[str, int]]]:
"""Test UDP ASSOCIATE command"""
try:
# UDP ASSOCIATE request
# VER(0x05) + CMD(0x03) + RSV(0x00) + ATYP(0x01) + DST.ADDR(0.0.0.0) + DST.PORT(0)
udp_request = b"\x05\x03\x00\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00"
self.sock.send(udp_request)
response = self.sock.recv(10)
if len(response) < 10:
print("❌ Incomplete UDP ASSOCIATE response")
return False, None
# Parse response
ver, rep, rsv, atyp = struct.unpack("!BBBB", response[:4])
if ver != 0x05:
print(f"❌ Invalid SOCKS version in response: {ver}")
return False, None
if rep == 0x00:
print("✅ UDP ASSOCIATE command accepted")
# Parse relay address and port
if atyp == 0x01: # IPv4
relay_ip = socket.inet_ntoa(response[4:8])
relay_port = struct.unpack("!H", response[8:10])[0]
print(f"✅ UDP relay endpoint: {relay_ip}:{relay_port}")
return True, (relay_ip, relay_port)
else:
print(f"❌ Unsupported address type in response: {atyp}")
return False, None
else:
error_messages = {
0x01: "General SOCKS server failure",
0x02: "Connection not allowed by ruleset",
0x03: "Network unreachable",
0x04: "Host unreachable",
0x05: "Connection refused",
0x06: "TTL expired",
0x07: "Command not supported",
0x08: "Address type not supported",
}
error_msg = error_messages.get(rep, f"Unknown error code: {rep}")
print(f"❌ UDP ASSOCIATE failed: {error_msg}")
return False, None
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ UDP ASSOCIATE test failed: {e}")
return False, None
def test_udp_relay(self, relay_endpoint: Tuple[str, int]) -> bool:
"""Test actual UDP relay functionality"""
try:
relay_ip, relay_port = relay_endpoint
# Create UDP socket for testing
udp_sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
udp_sock.settimeout(5)
# Create SOCKS5 UDP packet for DNS query to 8.8.8.8:53
# RSV(0x0000) + FRAG(0x00) + ATYP(0x01) + DST.ADDR + DST.PORT + DATA
dns_query = b"\x12\x34\x01\x00\x00\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x06google\x03com\x00\x00\x01\x00\x01"
socks_udp_packet = struct.pack(
"!HBB", 0x0000, 0x00, 0x01
) # RSV + FRAG + ATYP
socks_udp_packet += socket.inet_aton("8.8.8.8") # DST.ADDR
socks_udp_packet += struct.pack("!H", 53) # DST.PORT
socks_udp_packet += dns_query # DATA
print(
f"🔄 Testing UDP relay by sending DNS query through {relay_ip}:{relay_port}"
)
udp_sock.sendto(socks_udp_packet, (relay_ip, relay_port))
# Try to receive response
try:
response, addr = udp_sock.recvfrom(4096)
print(f"✅ Received UDP response from relay ({len(response)} bytes)")
print(f"✅ UDP relay is working correctly!")
return True
except socket.timeout:
print("❌ No response from UDP relay (timeout)")
return False
finally:
udp_sock.close()
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ UDP relay test failed: {e}")
return False
def test_proxy(self) -> dict:
"""Run complete UDP support test"""
auth_str = f"{self.username}:{self.password}@" if self.username else ""
result = {
"proxy": f"{auth_str}{self.proxy_host}:{self.proxy_port}",
"connection": False,
"udp_associate": False,
"udp_relay": False,
"relay_endpoint": None,
}
print(f"\n🔍 Testing SOCKS5 proxy: {self.proxy_host}:{self.proxy_port}")
print("=" * 50)
# Test connection and authentication
if not self.connect_and_authenticate():
return result
result["connection"] = True
# Test UDP ASSOCIATE command
udp_supported, relay_endpoint = self.test_udp_associate()
result["udp_associate"] = udp_supported
result["relay_endpoint"] = relay_endpoint
if not udp_supported:
return result
# Test actual UDP relay functionality
if relay_endpoint:
relay_works = self.test_udp_relay(relay_endpoint)
result["udp_relay"] = relay_works
return result
def close(self):
"""Close connection"""
if self.sock:
self.sock.close()
def parse_proxy_file(filename: str) -> list:
"""Parse proxy file with format username:password@ip:port"""
proxies = []
try:
with open(filename, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for line_num, line in enumerate(f, 1):
line = line.strip()
if not line or line.startswith("#"):
continue
try:
# Parse username:password@ip:port format
if "@" in line:
auth_part, addr_part = line.rsplit("@", 1)
if ":" in auth_part:
username, password = auth_part.split(":", 1)
else:
print(
f"⚠️ Line {line_num}: Invalid auth format, skipping: {line}"
)
continue
else:
# No authentication
username, password = None, None
addr_part = line
# Parse ip:port
if ":" in addr_part:
host, port_str = addr_part.rsplit(":", 1)
port = int(port_str)
else:
print(
f"⚠️ Line {line_num}: Invalid address format, skipping: {line}"
)
continue
proxies.append(
{
"host": host,
"port": port,
"username": username,
"password": password,
"original_line": line,
}
)
except ValueError as e:
print(f"⚠️ Line {line_num}: Error parsing line '{line}': {e}")
continue
except Exception as e:
print(
f"⚠️ Line {line_num}: Unexpected error parsing line '{line}': {e}"
)
continue
print(f"📖 Loaded {len(proxies)} proxies from {filename}")
return proxies
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"❌ File not found: {filename}")
print("📝 Please create proxy.txt with format: username:password@ip:port")
print("📝 Example content:")
print(" test:[email protected]:1080")
print(" XxoWb:[email protected]:1026")
print(" # Lines starting with # are ignored")
print(" 127.0.0.1:1080 # No auth proxy")
return []
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error reading proxy file: {e}")
return []
def test_multiple_proxies(proxy_file: str = "proxy.txt"):
"""Test multiple SOCKS5 proxies for UDP support"""
proxies = parse_proxy_file(proxy_file)
if not proxies:
return []
results = []
for proxy_config in proxies:
tester = SOCKS5UDPTester(
proxy_config["host"],
proxy_config["port"],
proxy_config.get("username"),
proxy_config.get("password"),
)
try:
result = tester.test_proxy()
results.append(result)
finally:
tester.close()
# Print summary
print("\n" + "=" * 80)
print("📊 SUMMARY")
print("=" * 80)
for result in results:
proxy_str = result["proxy"]
if result["connection"]:
if result["udp_associate"] and result["udp_relay"]:
status = "✅ FULL UDP SUPPORT"
elif result["udp_associate"]:
status = "⚠️ UDP ASSOCIATE ONLY (relay not working)"
else:
status = "❌ NO UDP SUPPORT"
else:
status = "❌ CONNECTION FAILED"
print(f"{proxy_str:<35} | {status}")
return results
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("SOCKS5 UDP Support Tester")
print("=" * 80)
# Check if custom proxy file specified
proxy_file = "proxy.txt"
if len(sys.argv) > 1:
proxy_file = sys.argv[1]
print(f"📂 Reading proxies from: {proxy_file}")
try:
results = test_multiple_proxies(proxy_file)
if results:
# Count results
total = len(results)
working_udp = sum(
1 for r in results if r["udp_associate"] and r["udp_relay"]
)
partial_udp = sum(
1 for r in results if r["udp_associate"] and not r["udp_relay"]
)
no_udp = sum(
1 for r in results if r["connection"] and not r["udp_associate"]
)
failed = sum(1 for r in results if not r["connection"])
print(f"\n📈 STATISTICS")
print("=" * 80)
print(f"Total proxies tested: {total}")
print(f"✅ Full UDP support: {working_udp}")
print(f"⚠️ Partial UDP support: {partial_udp}")
print(f"❌ No UDP support: {no_udp}")
print(f"💥 Connection failed: {failed}")
else:
print("\n❌ No proxies to test. Please check your proxy file.")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\n❌ Test interrupted by user")
sys.exit(1)
except Exception as e:
print(f"\n❌ Unexpected error: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
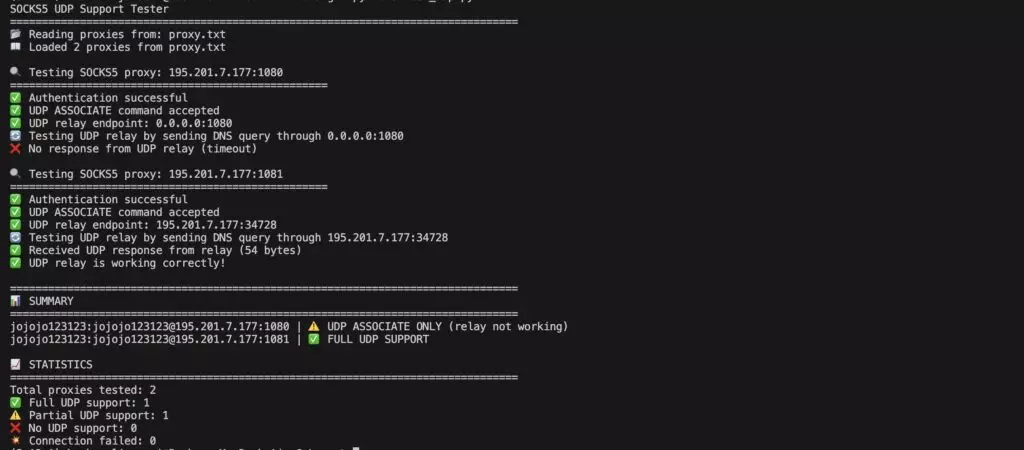
Here we tested two different proxies and found that one supports UDP and the other does not.
Conclusion
We hope that over the course of this article you’ve learned that testing UDP doesn’t have to be difficult or confusing. By using some strategically chosen methods we can, in a straightforward way, set up a SOCKS5 server and proxy UDP traffic through it.
Key Takeaways:
- Use tun2socks to create a virtual interface that will forward your traffic over a SOCKS5 proxy.
- Run a DNS lookup using
dig @8.8.8.8 google.com - On Linux: Test UDP via
sudo ntpd -q time.google.com - Test UDP over SOCKS by connecting to a Discord voice channel.
- Use our custom script to test your proxies at scale.
Between running a DNS lookup, syncing your clock via NTP, joining a Discord voice channel, and using a custom script, we’ve given you a range of options to test UDP over SOCKS.




