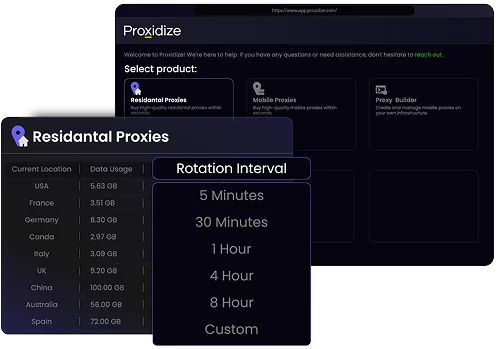
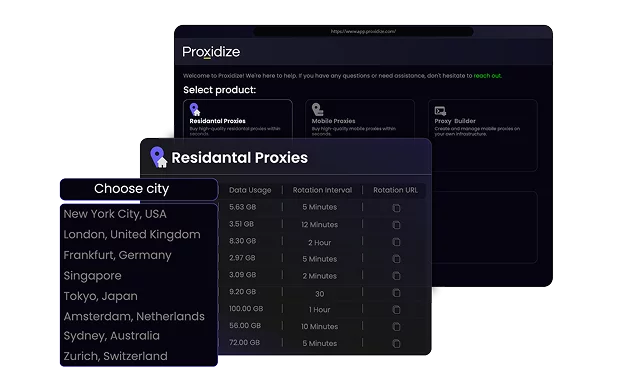
Proxidize residential proxies are designed for professionals and businesses that require high-performance IPs for tasks like web automation, data collection, quality assurance, and location-based testing. They are built to support consistent performance, scalability, and precise control.